The Ultimate Guidebook to Turnarounds
In the industrial sector, regular maintenance and upgrades are crucial to ensure the optimal performance, safety, and longevity of facilities. One of the most critical maintenance activities is the turnaround, a planned period of non-production during which plants carry out various inspection, repair, and replacement tasks. Turnarounds play a vital role in minimizing operational risks, maximizing efficiency, and ensuring regulatory compliance. They also provide an opportunity for companies to implement new technologies and process improvements, further enhancing their competitive edge.
Given the complexity and high stakes involved, executing a successful turnaround requires careful planning, skilled personnel, and efficient management. As a leader in the field, NOOTER is committed to providing expert turnaround services that help clients achieve their operational objectives while maintaining the highest safety and quality standards.
Overview
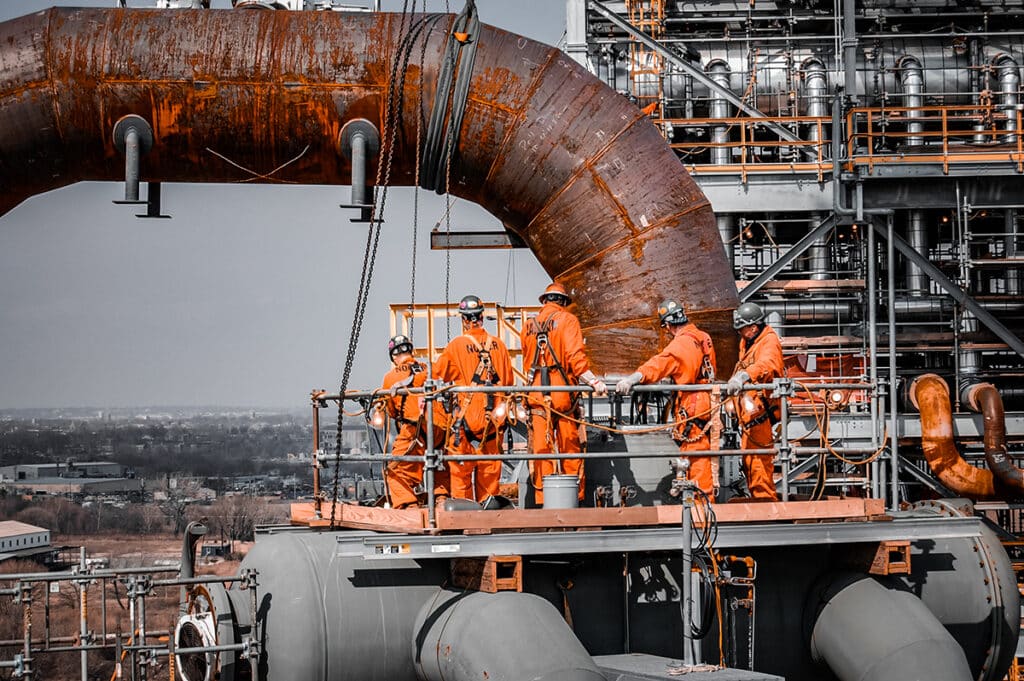

The Ultimate Guidebook to Turnarounds aims to serve as a comprehensive resource for industry professionals seeking to better understand the intricacies of turnarounds and implement best practices in their facilities.
In this guide, we will explore:
-
The nature and purpose of turnarounds, and their significance in the industrial sector
-
The key phases of a turnaround, including planning, execution, and post-turnaround evaluation
-
Essential elements of turnaround planning, such as scope definition, scheduling, budgeting, and safety considerations
-
Strategies for ensuring successful turnaround execution, including project management, communication, and quality control
-
Post-turnaround evaluation and continuous improvement processes
-
Best practices and strategies for maximizing the efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness of turnarounds
-
Emerging trends, innovations, and the role of digital technology in shaping the future of turnaround services
By the end of this guidebook, you will have a thorough understanding of the turnaround process, along with the knowledge and tools necessary to plan and execute successful turnarounds in your facility.
Let’s dive in!
Understanding Turnarounds
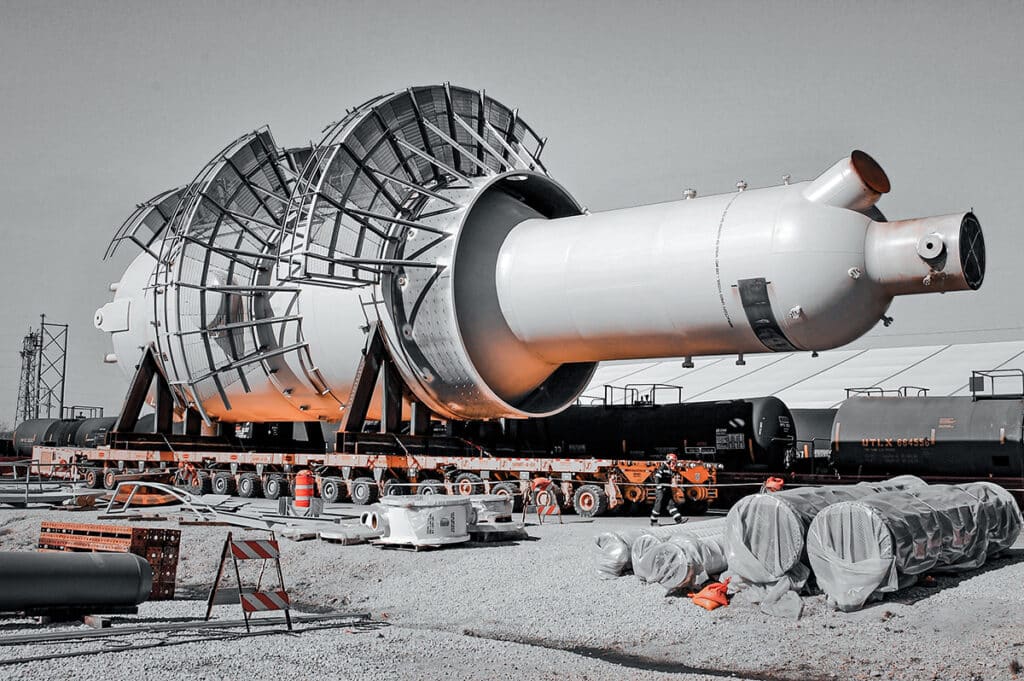

A turnaround is a planned period of non-production during which industrial facilities, such as refineries, chemical plants, and power generation plants, perform maintenance, inspection, repair, and upgrade activities.
The primary purpose of a turnaround is to ensure the continued safe, efficient, and reliable operation of the facility. Regular turnarounds help prevent equipment failures, reduce the risk of accidents, and maintain regulatory compliance. In addition, turnarounds present an opportunity for companies to implement process improvements, integrate new technologies, and optimize their operations.
Types of Turnarounds
Turnarounds can be categorized into three main types, depending on the factors that initiate them:
-
Planned Turnarounds: These are pre-scheduled events, typically conducted at regular intervals, based on the facility’s maintenance plan, equipment lifecycles, and industry guidelines. Planned turnarounds allow companies to perform preventive maintenance, replace worn-out equipment, and upgrade their facilities in an organized and efficient manner.
-
Unplanned Turnarounds: Unplanned turnarounds are triggered by unexpected events or equipment failures that necessitate immediate attention. These turnarounds can be more challenging to manage due to their unpredictability and the need for rapid response.
-
Emergency Turnarounds: Emergency turnarounds are required when a critical issue, such as a safety hazard or significant equipment failure, poses an immediate threat to the facility, personnel, or the environment. In such cases, the facility may need to shut down operations urgently to address the issue and prevent further damage or accidents.
Factors That Influence Turnaround Frequency and Duration
Several factors influence the frequency and duration of turnarounds, including:
-
Equipment Age and Condition: Older equipment typically requires more frequent maintenance and may necessitate longer turnarounds to address wear and tear.
-
Regulatory Requirements: Industry regulations and standards often dictate the minimum frequency of turnarounds to ensure compliance and maintain safe operations.
-
Facility Size and Complexity: Larger and more complex facilities usually require more time for thorough inspection, maintenance, and upgrades, resulting in longer turnaround durations.
-
Process and Technology Upgrades: The need to implement new technologies or process improvements may prompt companies to schedule more frequent or longer turnarounds.
-
Historical Performance and Lessons Learned: Companies often analyze past turnarounds to identify areas for improvement and adjust their turnaround schedules and durations accordingly.
By understanding the different types of turnarounds and the factors that influence their frequency and duration, facility operators can develop more effective maintenance plans and ensure the ongoing success of their operations.
The Turnaround Lifecycle
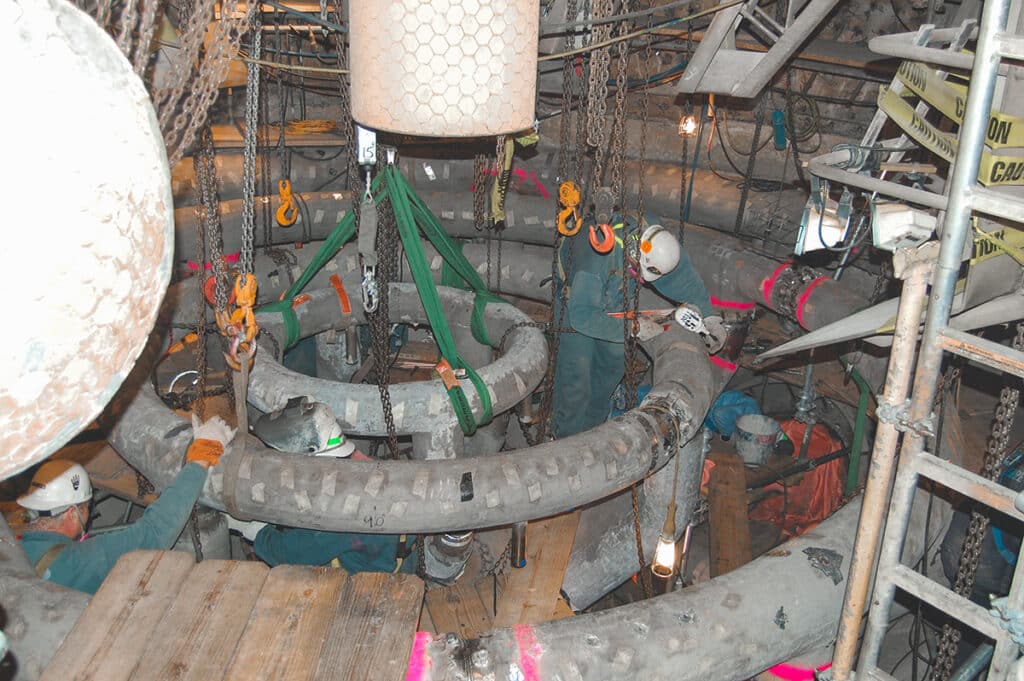

The turnaround lifecycle consists of three distinct phases: planning, execution, and evaluation. Each phase plays a crucial role in ensuring a successful turnaround, and careful attention to the key activities and milestones within each phase can significantly improve the overall efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness of the process.
Phase 1: Planning Phase
The planning phase is the foundation of a successful turnaround. It involves defining the scope of work, assessing risks, and developing a detailed plan that outlines the tasks, timelines, resources, and budget required.
Key activities and milestones in the planning phase include:
-
Scope definition: Identify the equipment and systems that require maintenance, repair, or upgrades during the turnaround.
-
Risk assessment: Evaluate potential risks associated with the turnaround, such as safety hazards, environmental impacts, and schedule delays.
-
Schedule development: Create a comprehensive and realistic schedule that allocates sufficient time for each task while minimizing downtime.
-
Budget estimation: Estimate the costs associated with the turnaround, including labor, materials, equipment rentals, and contingency funds.
-
Resource allocation: Determine the personnel, equipment, and materials needed for the turnaround, and secure their availability.
-
Safety and environmental planning: Develop safety and environmental plans to ensure compliance with regulations and minimize risks during the turnaround.
Phase 2: Execution Phase
The execution phase involves carrying out the tasks outlined in the planning phase while ensuring that work is completed safely, efficiently, and according to the established schedule and budget.
Key activities and milestones in the execution phase include:
-
Mobilization: Assemble the turnaround team, equipment, and materials at the facility, and conduct safety briefings and orientation sessions.
-
Task execution: Perform maintenance, repair, and upgrade tasks according to the plan, ensuring that quality and safety standards are met.
-
Progress monitoring: Track the progress of tasks against the schedule and budget, and address any deviations or issues that arise.
-
Change management: Handle any unexpected changes or challenges that emerge during the turnaround, such as scope adjustments, schedule revisions, or resource reallocations.
-
Demobilization: Upon completion of the turnaround, demobilize the team and equipment and restore the facility to normal operations.
Phase 3: Evaluation Phase
The evaluation phase occurs after the turnaround has been completed and involves assessing the success of the event, identifying lessons learned, and implementing improvements for future turnarounds.
Key activities and milestones in the evaluation phase include:
-
Performance assessment: Review key performance indicators (KPIs) to evaluate the success of the turnaround, such as safety incidents, schedule adherence, and budget performance.
-
Lessons learned: Conduct a thorough debriefing with the turnaround team to identify areas for improvement, best practices, and lessons learned.
-
Continuous improvement: Implement changes to the facility’s maintenance and turnaround plans based on the insights gained from the evaluation phase, to enhance future turnaround performance.
By understanding the turnaround lifecycle and effectively managing the key activities and milestones in each phase, facility operators can maximize the success of their turnarounds and ensure the safe, efficient, and reliable operation of their facilities.
Essential Elements of Turnaround Planning

Turnaround planning is a critical aspect of the turnaround lifecycle, setting the foundation for a successful event.
The following essential elements must be carefully considered and addressed during the planning phase to ensure a safe, efficient, and cost-effective turnaround:
Scope Definition and Risk Assessment
Defining the scope of work is the first step in turnaround planning. It involves identifying the equipment and systems that require maintenance, repair, or upgrades during the event. A thorough scope definition helps minimize the risk of unexpected issues or delays during the execution phase. Additionally, a comprehensive risk assessment should be conducted to evaluate potential safety hazards, environmental impacts, and other risks associated with the turnaround, allowing for appropriate mitigation measures to be incorporated into the plan.
Developing a Realistic Schedule
Creating a realistic schedule is crucial for managing expectations and allocating sufficient time for each task while minimizing downtime. The schedule should take into account factors such as equipment lead times, resource availability, and potential bottlenecks in the process. It’s also important to build in contingencies for unexpected issues or delays that may arise during the turnaround.
Budgeting and Cost Estimation
Accurate budgeting and cost estimation are essential for ensuring the financial success of the turnaround. Costs associated with labor, materials, equipment rentals, and other expenses should be carefully calculated and tracked throughout the project. A contingency fund should also be included in the budget to cover unexpected expenses or changes in scope.
Resource Allocation and Personnel Management
Determining the personnel, equipment, and materials required for the turnaround is a key component of the planning phase. This includes identifying the required skill sets, estimating the number of workers needed, and sourcing the necessary equipment and materials. Effective personnel management is also crucial for maintaining a productive and safe work environment. This includes clear communication of roles and responsibilities, proper training and orientation, and ongoing supervision and support.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Ensuring the safety of all personnel involved in the turnaround and minimizing environmental impacts are top priorities during the planning phase. A comprehensive safety plan should be developed that addresses potential hazards, establishes safety protocols, and provides training and resources to ensure a safe working environment. Environmental considerations, such as waste management, emissions control, and regulatory compliance, should also be incorporated into the plan.
By carefully addressing these essential elements during the turnaround planning phase, facility operators can lay the groundwork for a successful event that achieves its objectives while maintaining the highest standards of safety, quality, and cost-effectiveness.
Successful Turnaround Execution

Once the planning phase is completed, the focus shifts to the successful execution of the turnaround. This stage involves implementing the established plan, monitoring progress, adapting to changes, and ensuring the highest levels of work quality and safety.
The following are key elements that contribute to successful turnaround execution:
Effective Project Management and Communication
Project management is crucial during the execution phase. It involves coordinating activities, managing resources, and ensuring that tasks are completed on schedule and within budget. This requires clear and effective communication among all team members, including management, supervisors, workers, and other stakeholders. Regular meetings, progress reports, and digital communication tools can help facilitate information sharing and collaboration.
Ensuring Work Quality and Adherence to Safety Standards
Maintaining high work quality is essential to prevent future operational issues and ensure the longevity of the facility’s equipment. This involves following industry standards and best practices, conducting quality checks, and addressing any quality issues promptly. Equally important is adherence to safety standards to protect personnel and the environment. This includes enforcing safety protocols, providing appropriate personal protective equipment, and fostering a safety-conscious culture.
Monitoring Progress and Making Adjustments as Needed
Monitoring the progress of the turnaround against the established schedule and budget allows for early detection of deviations and timely corrective action. Key performance indicators (KPIs) should be tracked to evaluate performance and identify areas for improvement. In addition, flexibility is crucial during the execution phase. Despite the best planning, changes may be necessary due to unexpected findings, equipment failures, or other unforeseen circumstances. Being able to adjust the plan swiftly and efficiently is key to keeping the turnaround on track.
Managing Unexpected Issues and Changes
Despite thorough planning, unexpected issues or changes are likely to occur during a turnaround. Effective change management involves anticipating potential issues, implementing contingency plans, and making swift decisions to minimize their impact. This might involve adjusting work schedules, reallocating resources, or revising the scope of work.
By focusing on these key elements, facility operators can significantly increase the likelihood of a successful turnaround execution, ensuring that the facility is returned to full operational status as quickly, safely, and efficiently as possible.
Post-Turnaround Evaluation and Continuous Improvement

After the completion of a turnaround, it’s vital to conduct a post-turnaround evaluation. This phase focuses on assessing the success of the event, identifying lessons learned, and finding opportunities for improvement for future turnarounds.
The following elements are critical to this process:
Assessing the Success of the Turnaround Based on Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
The success of a turnaround is typically measured using a variety of key performance indicators (KPIs). These might include safety metrics (such as number of incidents), operational metrics (such as adherence to schedule and budget), and quality metrics (such as number of reworks required). By comparing actual performance against these KPIs, you can objectively assess the success of the turnaround.
Identifying Lessons Learned and Opportunities for Improvement
A thorough debriefing should be conducted after the turnaround to identify lessons learned and areas for improvement. This process should involve all team members, as each can provide valuable insights from their perspective. Topics to discuss might include what went well, what challenges were encountered, and what could be done differently in the future. By capturing these lessons learned, you can continuously improve your turnaround process.
Updating Maintenance and Turnaround Plans for Future Events
The insights gained from the post-turnaround evaluation should be used to update your maintenance and turnaround plans. This might involve adjusting the frequency of certain maintenance activities, revising your risk assessment process, improving your scheduling methods, or enhancing your safety protocols. By continuously refining your plans based on real-world experience, you can ensure that your future turnarounds are even more successful.
Through a detailed post-turnaround evaluation and a commitment to continuous improvement, organizations can enhance their turnaround performance over time, leading to increased efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Best Practices and Strategies for Turnaround Success

Achieving turnaround success requires adherence to best practices and the implementation of effective strategies that maximize efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
Top tips for maximizing turnaround efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness:
-
Start Early: Begin planning well in advance of the turnaround date. This allows ample time to define the scope, assess risks, and develop a detailed plan.
-
Define Clear Roles and Responsibilities: Ensure that every team member understands their roles, responsibilities, and expectations.
-
Foster Effective Communication: Keep lines of communication open and clear among all stakeholders, ensuring everyone is informed and aligned.
-
Prioritize Safety: Safety should be a core value throughout the turnaround process. Invest in safety training and establish strict safety protocols.
-
Use Technology: Utilize digital tools and technologies to streamline processes, enhance collaboration, and improve data tracking and reporting.
-
Incorporate Contingencies: Always plan for unexpected delays and issues. Include contingencies in your schedule and budget to accommodate unforeseen changes.
-
Continually Monitor and Adjust: Regularly track progress against the plan and make necessary adjustments in response to real-time developments.
By following these best practices and strategies, facility operators can significantly enhance their turnaround performance, ensuring the ongoing safety, reliability, and efficiency of their operations.
The Future of Turnarounds

As we look toward the future, turnarounds will continue to evolve in response to emerging trends, technological innovations, and the challenges and opportunities presented by Industry 4.0.
Here’s a glimpse into what the future might hold for turnaround services:
Emerging Trends and Innovations Shaping Turnaround Services
A number of trends and innovations are set to shape the future of turnaround services. These include increased use of predictive maintenance tools, the application of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) in risk assessment and scheduling, and the adoption of modular construction techniques to minimize on-site work. As sustainability becomes a higher priority, we can also expect to see more eco-friendly practices incorporated into turnarounds, such as waste reduction initiatives and energy-efficient technologies.
The Rise of Automated Welding in Turnarounds
One of the most promising developments in turnaround services is the rise of automated welding. Automated welding systems can significantly improve the efficiency, quality, and safety of welding tasks during turnarounds. By automating repetitive and complex welding procedures, facilities can not only speed up turnaround times but also reduce the risk of human error and enhance the overall quality of work. Moreover, automated welding can alleviate the pressure of skilled labor shortages, a common challenge in the industry.
See: The Advantages and Applications of Automated Welding Technology
The Role of Digital Technology in Improving Turnaround Processes
Digital technology is poised to play an increasingly important role in turnaround processes. The use of digital twin technology, for example, can improve planning and execution by providing a virtual representation of a facility for simulation and analysis. Similarly, Internet of Things (IoT) devices can provide real-time data on equipment performance, enabling proactive maintenance and reducing the likelihood of unexpected failures. Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies can also enhance safety training and provide assistance during complex tasks.
Preparing for the Challenges and Opportunities of Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0, characterized by the fusion of physical and digital technologies, presents both challenges and opportunities for turnarounds. On one hand, the increasing complexity of equipment and systems can make turnarounds more challenging. On the other hand, the availability of advanced technologies can improve turnaround efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. To prepare for Industry 4.0, facility operators will need to invest in new skills and capabilities, embrace digital transformation, and adopt a culture of continuous learning and innovation.
By staying ahead of these trends and harnessing the power of emerging technologies, companies can ensure their turnaround services remain competitive, efficient, and effective in the future.
Conclusion

As we wrap up this comprehensive guidebook to turnarounds, let’s revisit some of the key takeaways:
-
Understanding the definition, purpose, and types of turnarounds is foundational to managing them effectively.
-
The turnaround lifecycle consists of three phases: planning, execution, and evaluation. Each phase involves key activities and milestones that contribute to the success of the turnaround.
-
Essential elements of turnaround planning include scope definition and risk assessment, realistic scheduling, budgeting and cost estimation, resource allocation, and safety and environmental considerations.
-
Successful turnaround execution relies on effective project management, work quality and safety adherence, progress monitoring, and adept management of unexpected changes.
-
Post-turnaround evaluation provides an opportunity for continuous improvement by assessing success, identifying lessons learned, and updating plans for future turnarounds.
-
Best practices and strategies for maximizing turnaround success include early planning, clear role definition, effective communication, safety prioritization, technology utilization, contingency planning, and continual progress monitoring.
-
Future trends in turnarounds involve the increasing role of digital technology and the challenges and opportunities of Industry 4.0.
As a trusted name in the industry since 1896, NOOTER remains committed to providing expert turnaround services and solutions. Our extensive experience and dedication to innovation position us as leaders in executing safe, efficient, and cost-effective turnarounds. We embrace the opportunities and challenges of the future with a constant commitment to improving our services and delivering exceptional results for our clients.
Thank you for joining us on this comprehensive exploration of turnarounds. We hope you found this guidebook informative and valuable as you navigate your own turnaround processes.
Explore NOOTER’s Expert Turnaround Services

Whether you’re facing an upcoming turnaround or planning for future maintenance events, the team at NOOTER is ready to support your journey.
With over a century of experience in industrial construction and maintenance, we offer top-tier turnaround services that prioritize safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness.
Contact us today to learn how we can help optimize your turnaround processes and drive your business toward success.